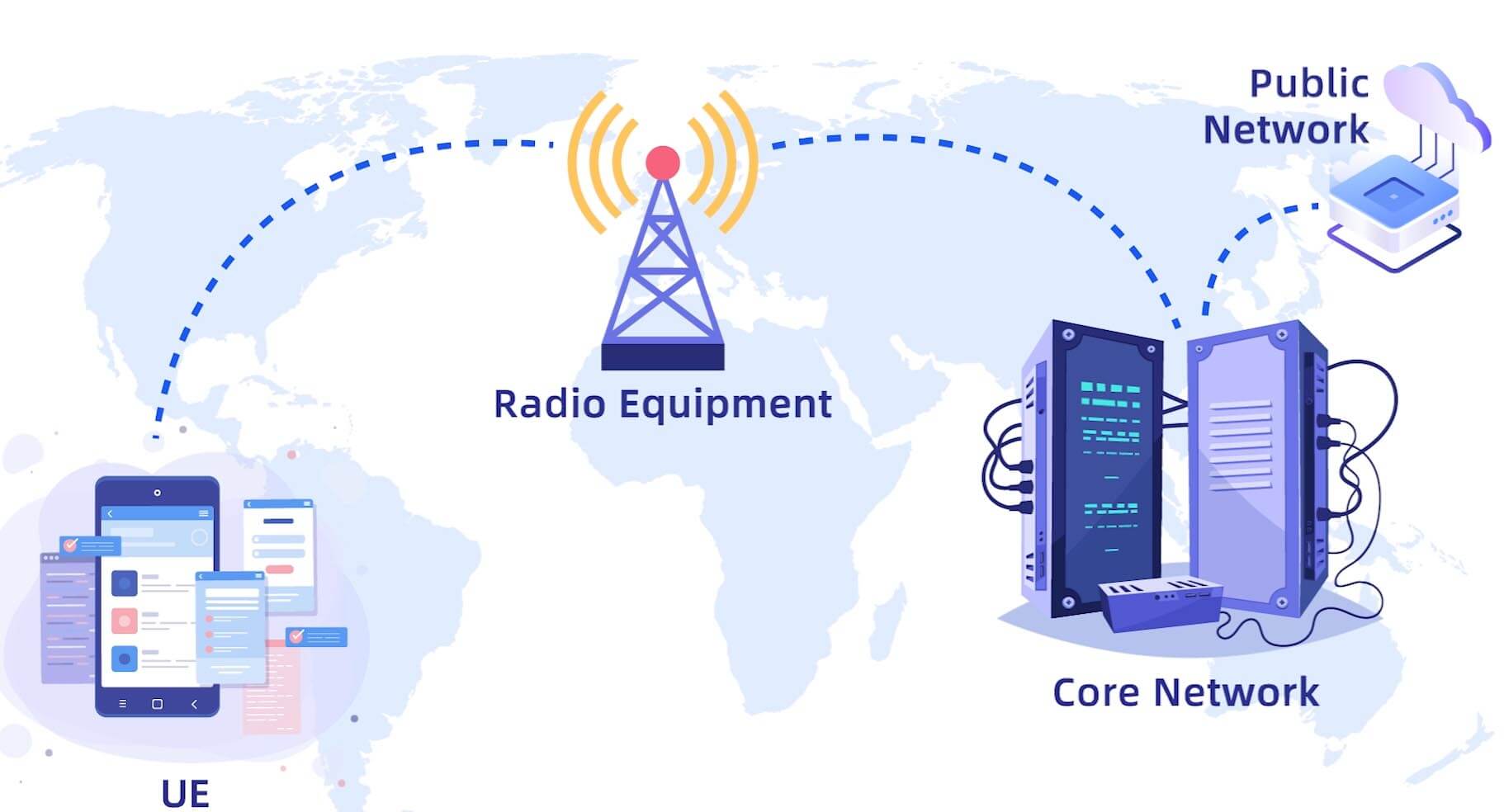
Core Networks
core networks play a central role in facilitating communication and data transfer between users. The core network is a key component of a telecommunications infrastructure and is responsible for managing and routing voice, data, and multimedia traffic across a service provider's network. Here's a general description of core networks in telecom:
- Centralized Control and Management:
- Core networks are designed to provide centralized control and management of communication services. They handle tasks such as call setup, call routing, and connection management.
- Data Transmission:
- Core networks enable the transmission of data between different devices and networks. This includes voice data (for traditional telephone services), text messages, multimedia messages, and internet data.
- Network Interconnection:
- Core networks facilitate the interconnection of various access networks, such as mobile networks, fixed-line networks, and internet networks. This allows for seamless communication between users on different types of networks.
- Routing and Switching:
- Core networks use sophisticated routing and switching mechanisms to efficiently direct data packets from the source to the destination. This involves making decisions about the most optimal paths for data transmission.
- Protocol Conversion:
- Core networks often involve protocol conversion to ensure compatibility between different types of networks and devices. This is crucial for supporting diverse communication services.
- Traffic Management:
- Core networks are responsible for managing the flow of traffic, ensuring that resources are used efficiently, and optimizing the overall performance of the network.
- Quality of Service (QoS):
- Core networks implement mechanisms to ensure the quality of service, which involves maintaining a certain level of performance for various types of communication services. This includes factors such as low latency, high bandwidth, and minimal packet loss.
- Security:
- Security is a critical aspect of core networks. They incorporate various measures to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats.
- Support for Various Services:
- Core networks are designed to support a wide range of services, including voice calls, video calls, messaging, internet access, and other multimedia services.
- Scalability:
- Core networks are built with scalability in mind to accommodate the growing number of users and the increasing demand for data services. This involves the ability to expand network capacity and adapt to changing requirements.
In summary, core networks form the backbone of telecommunications infrastructure, providing the essential functions needed for efficient and reliable communication services. They are integral to connecting users across different networks and supporting a diverse range of communication applications.
