IP Networks
IP networks play a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of data between various devices and systems. Here's a general description of IP networks in telecom:
- Definition:
- IP (Internet Protocol): This is a set of rules that govern how data is sent and received over networks. In the context of telecom, IP networks use the Internet Protocol to enable communication between devices.
- Structure:
- Devices: IP networks consist of various devices such as computers, smartphones, routers, switches, and servers. These devices communicate with each other using IP addresses.
- Infrastructure: The network infrastructure includes routers and switches that manage the flow of data between devices. These devices are often interconnected through a combination of wired and wireless technologies.
- Protocols:
- TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): This is the fundamental suite of protocols that govern communication on IP networks. TCP ensures reliable data delivery, while IP handles the addressing and routing of the data.
- Other Protocols: In addition to TCP/IP, various protocols such as UDP (User Datagram Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), and others are used for specific purposes within the IP network.
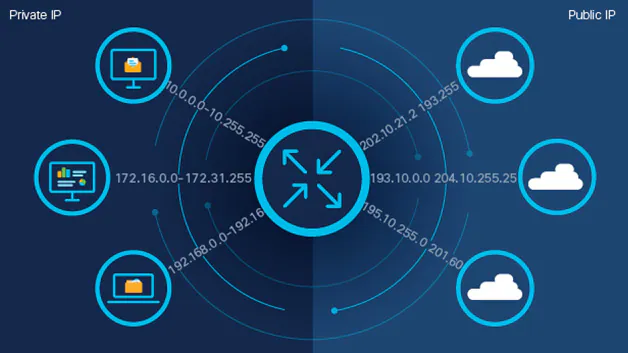
- Addressing:
- IP Addresses: Every device connected to an IP network is assigned a unique numerical label called an IP address. IP addresses are used for routing data to the correct destination within the network.
- IPv4 and IPv6: IP networks can use either IPv4 (32-bit addressing) or IPv6 (128-bit addressing) to accommodate the growing number of devices connected to the internet.
- Routing:
- Routing Tables: Routers within the IP network maintain routing tables, which are used to determine the best path for data to travel from the source to the destination. This involves making decisions based on IP addresses and network topology.
- Services:
- Internet Services: IP networks enable access to various internet services, including web browsing, email, streaming, and online collaboration tools.
- Voice and Video Communication: IP networks support Voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing, allowing for real-time communication over the internet.
- Security:
- Firewalls and Security Protocols: IP networks implement security measures such as firewalls, encryption, and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to protect data from unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of communications.
- Evolution:
- 5G and Beyond: As telecom technologies evolve, IP networks are adapting to support higher data speeds, low latency, and massive device connectivity, particularly with the deployment of 5G and future generations of mobile networks.
In summary, IP networks in telecom form the backbone of modern communication, enabling the exchange of data across a vast and interconnected landscape of devices and services.
